The nature of markets
- Outline the meaning of the term market.
A market is any effective arrangement for bring buyers and sellers together, not necessarily face-to-face, to enable trade to take place.
Consumers and Producers:
Consumers want to get the most from their money and wants the highest quality at the lowest price.
Producers want to get the most from their resources that they have, they want to sell as low a quality product as they can for as high a price as possible. A.k.a Profit Maximization.
Demand
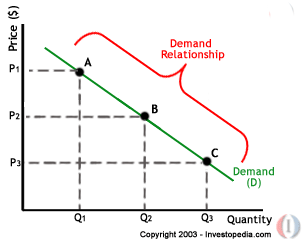
Define: Demand is that quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy at each and every price at a given period of time.
The law of demand
Define: The law of demand states "as the price of a product falls, the quantity demanded of a product will usually increase, ceteris paribus (Controlled variables)."
- Explain the negative casual relationship between price and quantity demanded
- Describe the relationship between and individual consumer's demand and market demand
The demand curve
- Explain that a demand curve represents the relationship between the price and the quantity demanded of a product, ceteris paribus.
- Draw a demand curve
- Explain how factors including changes in income (in the case of normal and inferior goods), preferences, prices of related goods (in the case of substitutes and complements) and demographic changes may change demand.
Movement along and shifts of the demand curve
- Distinguish between movement along the demand curve and shifts of the demand curve.
- Draw diagrams to show the difference between movements along the demand curve and shifts of the demand curves.
Supply
The law of supply
- Explain the positive casual relationship between price and quantity supplied
- Describe the relationship between an individual producer's supply and market supply
The supply curve
- Explain that a supply curve represents the relationship between the price and the quantity supplied of a product, ceteris paribus.
The non-price determinants of supply (factors that change supply or shifts the supply curve.
- Explain how factors including change in costs of factors of production (land, labour, capital and entrepreneurship), technology, price of related goods (joints/competitive supply), expectations, indirect taxes and subsidies and the number of firms in the market can change supply.
Movement along and shifts of the supply curve
- Distinguish between movements along the supply curve and shifts of the supply curve
- Construct diagrams to show the difference between movement along the supply curve and shifts of the supply curve.
Market Equilibrium
Equilibrium and changes to equilibrium
- Explain, using diagrams, how demand and supply interact to produce market equilibrium
- Analyse, using diagrams and with reference to excess demand or excess supply, how changes in the determinants of demand and/or supply result in a new market equilibrium.
The role of the price mechanism
Resource allocation
- Explain why scarcity necessities choices that answer the "What to produce?" question.
- Explain why choice results in an opportunity cost.
- Explain, using diagrams, that price has a signalling function and an incentive function, which result in a reallocation of resources which prices change as a result of a change in demand or supply conditions.
Market Efficiency
Consumer surplus
- Explain the concept of consumer surplus
- Identify consumer surplus on a demand and supply diagram
Producer surplus
- Explain the concept of producer surplus
- Identify producer surplus on a demand and supply diagram
Allocative Efficiency
- Explain that the best allocation of resources from society's point of view is at competitive market equilibrium, where social (community) surplus (consumer surplus and producer surplus) is maximized (marginal benefit = marginal cost)